Working principle and characteristics of liquid oxygen electrode
1 Introduction
Oxygen electrode is a polarographic electrode designed to measure the dissolved oxygen content in water. As early as 1930s, some people used bare silver-platinum electrode to study the photosynthesis of algae. Since the advent of the thin-film oxygen electrode in the 1950s, it has greatly expanded its scope of application. Because it has the advantages of high sensitivity, fast response, continuous measurement and recording, and the ability to track the dynamic change of the reaction, etc., in the study of photosynthetic oxygen release and respiratory oxygen consumption of chloroplast and mitochondrial suspension, certain oxygen consumption Or the study of enzymatic reaction of oxygen evolution has been widely used. In recent years, people have used this technique to measure the photosynthetic oxygen release of leaf fragments or free leaf cells, and have also achieved success. Now it has developed into a conventional technique for simple and rapid determination of dissolved oxygen.
Oxygen electrode can be used to study the photosynthesis of plant leaves and green parts, the measurement of the respiration rate and respiratory pathway of plants, animal tissues, organs and microorganisms, the determination of the integrity of isolated chloroplasts, the determination of the activity of RuBP oxygenase, plant tissues Determination of H2O2 enzyme activity, polyphenol oxidase activity, fatty acid oxidase activity in plant tissues and mitochondrial respiration.
2 Basic principle and structure of oxygen electrode
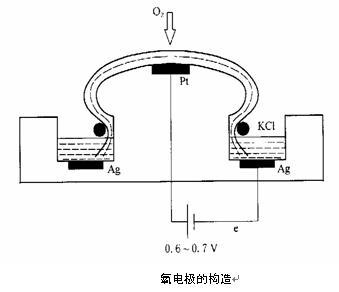
2.1 Structure of oxygen electrode
The thin film oxygen electrode was developed by LC Clark (1953), so it is also called Clark oxygen electrode. The oxygen electrode is actually an electrochemical cell (above), consisting of silver and platinum electrodes embedded in an insulating material. The silver electrode is generally made into a ring shape. As the reference electrode, the area of ​​the silver electrode should be as large as possible to reduce the current density on the electrode surface and reduce the polarization phenomenon of the anode, so that the electrode potential is not affected by the applied voltage influences. The platinum cathode is generally made into a dot shape and is located in the center of the silver pole. The electrolytic reaction occurs on the platinum pole.
The surface of the electrode is covered with a 15-20 μm polyethylene or polytetrafluoroethylene film, and a potassium chloride solution is filled between the electrode and the film as an electrolyte. Because dissolved oxygen in water can permeate the membrane and the electrolyte cannot penetrate, the interference of various ion electrolysis reactions in the tested solution is eliminated, and it becomes a special electrode for measuring dissolved oxygen.
2.2 Basic principle of oxygen electrode
When a voltage is applied between the two electrodes of the oxygen electrode and exceeds the decomposition voltage of O2 (about -0.2V), the dissolved oxygen that enters the potassium chloride solution through the film is reduced on the platinum cathode: O2 + 2H2 + 4e- = 4OH-
Silver oxidation occurs on the silver anode: 4Ag + 4Cl- = 4AgCl + 4e
At this time, an electrolytic current is generated between the electrodes. Since oxygen is reduced at the cathode, the concentration of oxygen on the surface of the cathode is reduced, so the dissolved oxygen in the measured solution diffuses and supplements to the cathode, so that the reduction process can continue, and because the speed of the electrode reaction is extremely fast, the oxygen molecule The diffusion rate is slower, so the size of the electrolytic current is limited by the diffusion rate of oxygen. This electrolytic current limited by the oxygen diffusion rate is called the diffusion current. When the solution is stationary and the temperature is constant, the diffusion current is controlled by the concentration difference between the measured solution and the electrode surface O2. As the applied voltage increases, the concentration of O2 on the electrode surface will inevitably decrease. The difference between the concentration of the measured solution and the surface of the electrode increases, and the diffusion current also increases. But when the applied polarization voltage reaches a certain value, the reduction rate of oxygen on the cathode surface greatly exceeds the diffusion rate of O2 to the cathode, making the concentration of O2 on the cathode surface approach zero, so the size of the diffusion current depends entirely on the solution being measured The concentration of oxygen (for the thin film oxygen electrode, that is, the concentration of O2 immediately outside the membrane). At this time, if the polarization voltage is increased again, the diffusion current will basically not increase any more, so that the polarographic wave (that is, the current-voltage curve) produces a flat top. Choosing the polarization voltage in the middle of the flat top (about 0.6 ~ 0.9V) can make the diffusion current basically independent of the small voltage fluctuations. That is, the voltage is between 0.6 and 0.9V, and there is a good linear relationship between the current output by the oxygen electrode and the oxygen concentration outside the electrode. Therefore, under the conditions of constant polarization voltage and temperature, the size of the diffusion current can be used as the basis for quantitative measurement of dissolved oxygen. The diffusion current signal generated between the electrodes can be converted into a voltage output through the circuit of the electrode controller and recorded with an automatic recorder.
The advantages and disadvantages of the oxygen electrode method: the oxygen electrode method is used to measure dissolved oxygen in water to study photosynthesis and respiration. It can solve some problems that cannot be solved or difficult to be solved by conventional detection techniques. Therefore, it is compared with the micro-pressure test technique (Varsonometer) The method has the following advantages:
A. The sensitivity is extremely high. The method can be used to detect dissolved oxygen in water, and its sensitivity can reach 2 × 10-3 ~ 4 × 10-3μmol / ml or 4 × 10-2 ~ 9 × 10-2μl / ml, which is higher than the micro-pressure test method. The sensitivity is more than 10 times higher.
B. Fast measurement One measurement can be completed within a few minutes.
C. It can quickly track the dynamics of the change of dissolved oxygen content, and can record the change process without leaking any small changes, and the micro pressure test method can not measure the instantaneous change of the gas exchange rate.
D. Use automatic recorder to record the results or computer control, easy to operate and high degree of automation.
Sublimation Heat Press Machines
Sublimation Heat Press Machines,Heat Press Printing Machine,Portable Heat Press Machine,Heat Transfer Machine Press
vchomy , https://www.jsvichen.com