One: EB coating curing is an energy curing principle. It is an advanced technology for surface processing of materials that emerged in the mid-20th century. It uses electron beams to initiate radiation-chemically active liquid materials (paints, inks, or adhesives) to rapidly polymerize and crosslink In order to achieve a new process of curing.
First, high-energy electrons interact with paint molecules to break them down into free radicals;
Then, the free radical reacts with the C = C double bond to form a growth chain;
Finally, the growth chain reacts with the remaining components of the paint, causing the paint to crosslink.
The picture below shows the mechanism of EB curing
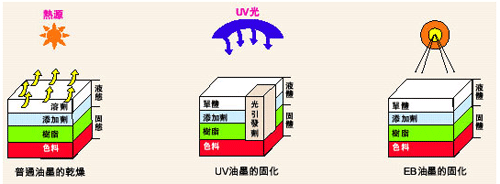
Two: Compared with traditional curing technology, EB curing has unique advantages
The curing time of the first EB coating is very short, generally only 1/10 second can be completely dried and fixed on the surface of the substrate. For traditional thermosetting coatings, the drying time may take several minutes or even a few days to completely dry, so Energy-curable coating products have high production efficiency and short delivery time. At present, the speed of EB curing production line abroad has exceeded 300m / min (Douglas-Hanson).
Second, it occupies less space. The EB equipment on the coating curing production line occupies only 4.3m, and the original thermal curing production line occupies 91.4m.
Third, cold solidification, without the thermal inertia of the system, the output power of the EB equipment can change with the speed of the production line. It is easy to operate, easy to control, and has high accuracy and repeatability.
Fourth EB curing can make the coating 100% cured.
Fifth, the energy-cured coating, because the chemicals in the coating form a polymer three-dimensional network polymer through cross-linking reaction, the surface has strong chemical resistance, friction resistance and weather resistance.
Sixth, the solid content of EB coating after curing is close to 100%, and it does not contain VOC (organic volatile matter). Compared with ordinary coating systems, it has no environmental pollution and is more environmentally friendly.
Seventh EB curing has no solvent volatilization, the cured film is uniform, and the surface is smooth and clean. Under the premise of satisfying the main performance, it has better performance and appearance than the thermal curing coating.
Eighth, low energy consumption, EB curing energy consumption is about 1% of traditional thermal curing.
Three: Comparison of total energy consumption and CO2 emission reduction of electron beam cured coatings and solvent-based cured coatings
System Solvent Type Electron Beam Curing Material
Paint solid content 60% 100%
Solid coating weight (g / m2) 20g 20g
VOCs / m2 (g) (solvent with a density of 0.9) 12g None
Strong wind system total energy consumption (kJ / m2)
(Calculated curing energy consumption is 27.3kJ / g) 328kJ None
Total energy consumption of electron beam curing (kJ / m2)
(30kGy or 0.030kJ / g, electron beam energy conversion rate 70%) None 0.86kJ
Total energy consumption per hour (11,200m2 per hour) ~ 3700,000kJ ~ 9,600kJ
Total energy consumption per hour 1030kWh 2.67kWh
CO2 emissions from solvent combustion and reuse 37g / m2
Total CO2 emission of the device 415.8kg / h
Plate width 1500mm, running speed 125m / min, coating thickness 20umm, output 11,250m2 / h
Performance of EB cured coating (domestic test)
At a voltage of 105keV and a current of 10mA.
The measured results of adhesion, flexibility, impact resistance, bending resistance, aging resistance, corrosion resistance and other indicators fully comply with ASTM D-3359, ASTM B-117, ASTM D-3363, ASTM D-3363, ASTM D-2794 , ASTM D-522, ASTM D-4145 standards.
Four: The production process is as follows
Thermal curing process
Uncoiler → Sewing machine → Press roller → Tension machine → Uncoiler looper → Alkali-eluting grease → Cleaning → Drying → Passivation → Drying → Initial coating → Initial coating drying → Topcoat fine coating → Topcoat drying → Air-cooled cooling → Winding looper → Winding machine → (The lower roll is packaged into the warehouse);
EB curing process
Uncoiler → Sewing machine → Press roller → Tension machine → Uncoiler looper → Alkali eluting grease → Cleaning → Drying → Passivation → Drying → Initial coating → Initial coating EB curing → Topcoat finishing → Topcoat EB curing → Air-cooled (water-cooled) temperature reduction (can be considered to be cancelled) → Winding looper → Winding machine → (The lower volume is packaged into the warehouse);
Five: EB curing applications abroad:
In the early 1970s, Ford Corporation of the United States applied EB curing technology to auto parts and instrument coatings for the first time, which created a precedent for the application of EB curing technology in industrial production. During the same period, Album Printing Company used EB curing inks and coatings on packaging materials.
Subsequently, it developed rapidly in regions and countries with developed industries and strong environmental awareness, such as Europe, North America, and Japan. According to statistics, in 2005, there were a total of 800 EB curing production lines in countries around the world, including more than 400 in the United States (55%), more than 300 in Japan (including scientific research and development) (38%), and 50-60 in Europe (7%) .
Six: Equipment principle:
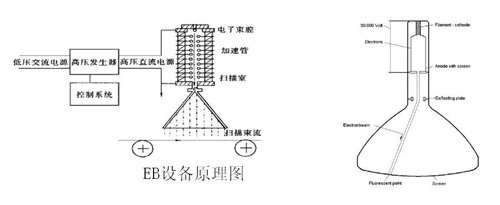
Fuzz Remover,Electric Fuzz Remover,Fabric Shaver Electric,Clothes Lint Remover
Ningbo Beilun Xuanfeng Molding Co., Ltd. , https://www.schelfern.com