1 Introduction:
In the current in vitro exposure study, the test compound can be directly contacted with cells at the gas-liquid interface (Cultex), which avoids the interference of the medium components in the traditional immersion culture exposure. The experimental reproducibility (stability and reproducibility) during in vitro exposure to this gas-liquid interface depends on the in vitro exposure of the cell and the optimal design of the exposure system.
In the literature, we have a different type of in vitro exposure to the test substance that is directly exposed to cell exposure at the gas-liquid interface (Aufderheide, 2005; Aufderheide et al., 2005). Here, we compare the experimental types of the two main application module types, the Linear Flow System and the Radial Flow System, to discuss the two methods. The difference.
2. Materials and methods
2.1 In vitro exposure to the system
2.1.1 CULTEX CG (Linear Flow Exposure System) The first generation of gas-liquid interface in vitro exposure system is shown in Figure 1. The main feature is the linear distribution of cell culture chamber and inlet aerosol inlet. Form a tight closed system. The bottom module is a cell culture part, and has a 37 ° C water bath and a flowable medium supply; the top is a linear gas inlet and outlet module corresponding to the culture chamber, and a negative pressure is achieved in the closed chamber through an air pump connected at the rear end, The required exposed substances are continuously discharged into the closed system to complete the exposure and are discharged from the rear end. A good cell culture environment is formed in the cell culture chamber, and the cells can be directly contacted with the gas coming in from the top to achieve direct gas-liquid interface exposure. The system is suitable for 12 mm cell culture chambers.
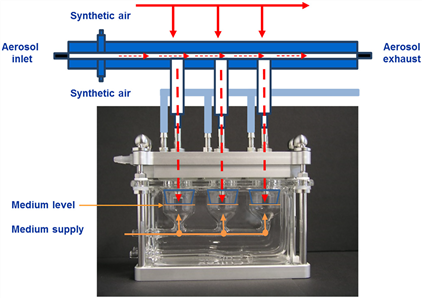
Figure 1 CULTEX CG (Linear Flow External Exposure System)
2.1.2 CULTEX RFS (Radial Flow System) The second-generation exposed gas-liquid interface in vitro exposure system (http://) is shown in Figure 2, Figure 3, is a completely new design of in vitro exposure Poison system module. A new type of radiation management gas path design: the cell culture (three or six) chambers in the bottom module are symmetrically distributed, and the inlets of the top module are directly divided into three (or six) inlets for radiation control distribution. The channel, after sealing, enters the gas and directly contacts the cells corresponding to the bottom chamber. At the same time, the system provides a sustainable flow medium and a 360-degree water bath to ensure an in vitro cell culture environment.
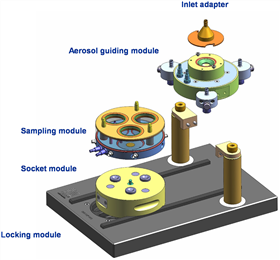
Figure 2 Appearance of CULTEX RFS for linear fluid exposure system

Figure 3 Schematic diagram of the CULTEX RFS structure of the linear fluid exposure system
2.1.3 CULTEX DG particulate aerosol generator (Wright 1950), fully automatic dry powder aerosol generator with feed rate of 800 U/min, airflow size of 8 L/min, exposure time and particle type see attached table 1.
Table 1 Main parameters of the experimental substance
substance
Buying a brand
Compression pressure [kg]
Compression time [s]
Feed rate [mm/h]
Density after compression [g/cm3]
Deposition quality / 30 min. [mg]
Pural 200
Sasol
450
3
0.98
1.22
220
Copper (II) oxide micro
Sigma Aldrich
450
3
2.43
2.35
189
Copper (II) oxide nano
Io-li-tec
450
3
1.95
2.20
198
2.1.4 Automatic Cigarette Smoke Generator, K3R4F Research Cigarette (University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY, USA), smoking parameters set 35 mL puff volume/2 s, 1 puff per minute, 7 puffs per cigarette, ventilation flow 1L /min.
2.1.5 Particulate Deposition, Particulate Deposition As shown in Figure 5, the particulate matter deposited in the cell compartment is on the glass fiber membrane (Type: MNGF-1; Machery-Nagel, Germany), and the glass fiber membrane is passed through Clip Fit (Fig. 4). The device was fixed in a cell culture chamber, and the test balance was weighed (SE2F Microbalance, readability: 0.1 mg; Sartorius GmbH, Germany).
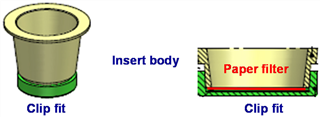
Figure 4 Clip Fit fixing bracket
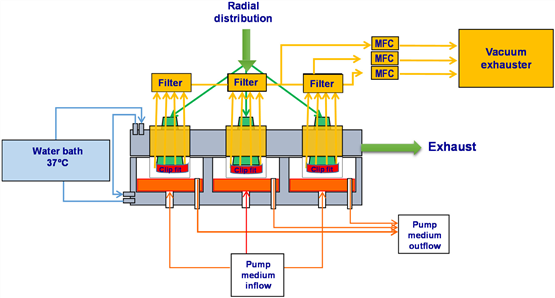
Figure 5 particle deposition mode diagram
3. Results
Particles of different particle sizes and qualities have different deposition results in two different exposure modules. In general, although the physicochemical properties and particle size of the particles may have an effect on the deposition of the particles, it can be seen from the exposure results of the same particles that the exposure data of the three locations in the CULTEX RFS exposed to the radiation flow system is lower. The deviation and relative standard deviation, and the relative standard deviation are within 5%. The relative standard deviations of the linear flow exposure system CULTEX CG were all greater than 10%, and the precision and the experimental parallelism and repeatability between the three channels were poor.
Table 2 Quality and analysis of deposition on glass fiber membranes after 30 minutes of Pural 200 exposure
Exposure module
Insert 1 [μg]
Insert 2 [μg]
Insert 3 [μg]
Arithmetic average [μg]
Deviation [%]
Radiation Fluid External Exposure System (Radial Flow System)
199
205
208
204
4
199
199
201
200
1
214
211
214
213
1
Linear Fluid System (Linear Flow System)
280
189
191
220
41
267
239
341
282
36
258
274
346
293
30
3.1 High Purity Alumina Pural 200
3.1.1 High Purity Alumina Pural 200 has a particle size ranging from 40 nm to 40 microns. The linear flow exposure system and the radiation flow exposure system are generated using the same aerosol generator. After the same exposure time, the glass fiber membranes were weighed separately before and after the exposure, and the weight of the deposited particles on the membrane was obtained in Table 2.
3.1.2 Experimental data of two exposure modules show that, on average, in the quality of particulate matter deposition, the linear flow exposure of the exposure system exceeds the radiation flow exposure exposure system. At the same time, however, the magnitude of the numerical change obtained by the three exposed exposure sites of the radiation flow exposure system was significantly reduced. This means that the three chambers of the radiation flow exposure exposure system can distribute the particles more equally, the parallelism between the channels is better, and the experiment repeatability and stability are better. To investigate this aspect, we further studied the other two granular compounds, copper oxide microparticles and copper oxide nanoparticles.
3.2 copper oxide microparticles
The particle size of the copper oxide particles is <5 mm. The experimental data are shown in Table 3. We observed that the deposition data in the radiation flow exposure system has very high reproducibility, while the data deviation of the linear flow exposure system deposition is quite large; 2. The difference in the distribution of particles deposited on the glass fiber membrane is very large. As shown in Fig. 6, the particles in the linear flow exposure system are mainly concentrated in the center of the film, while the particles in the radiation flow exposure system are distributed evenly on the entire film surface.
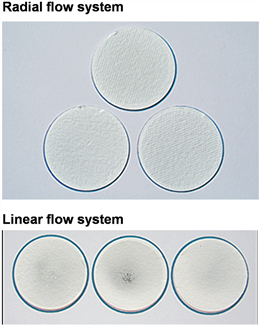
Figure 6 Deposition effect of copper oxide microparticles on glass fiber membrane
Table 3 Quality and analysis of deposition on glass fiber membranes after 30 minutes of exposure of copper oxide microparticles
Exposure module
Insert 1 [μg]
Insert 2 [μg]
Insert 3 [μg]
Arithmetic average [μg]
Deviation [%]
Radiation fluid external exposure system (Linear Flow System)
140
142
142
141
1
153
151
149
151
3
149
145
152
149
5
Linear Fluid System (Linear Flow System)
177
196
135
169
36
188
264
90
181
96
207
200
114
174
54
Table 4 Quality and analysis of deposition on glass fiber membranes after 30 minutes of exposure of copper oxide nanoparticles
Exposure module
Insert 1 [μg]
Insert 2 [μg]
Insert 3 [μg]
Arithmetic average [μg]
Deviation [%]
Radiation fluid external exposure system (Linear Flow System)
290
302
316
303
9
242
266
262
257
9
175
174
181
177
4
Linear Fluid System (Linear Flow System)
177
196
135
169
28
188
264
90
181
twenty one
207
200
114
174
13
3.3 copper oxide nanoparticles
The particle size of the copper oxide particles was <42 nm. The experimental data are shown in Table 4. A similar effect to the experiment of the copper oxide microparticles was observed. The data deviation of the linear flow exposure system deposition was much higher than that of the radiation flow exposure system, while the particles on the glass fiber membrane were larger. The deposition distribution of the radiation flow exposure system is more uniform as shown in Figure 7.
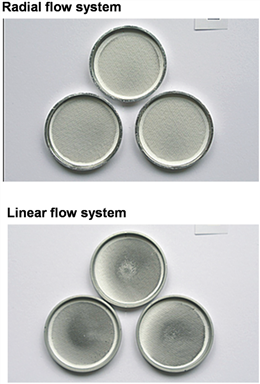
Figure 7 Deposition effect of copper oxide nanoparticles on glass fiber membrane
Table 5 Deposition quality and analysis of K3R4F flue gas particles on glass fiber membrane after exposure for 30 minutes
Exposure module
Insert 1 [μg]
Insert 2 [μg]
Insert 3 [μg]
Arithmetic average [μg]
Deviation [%]
Radiation fluid external exposure system (Linear Flow System)
87
86
87
87
1
81
83
86
83
6
75
73
79
76
8
88
83
85
85
6
81
80
82
81
2
82
81
83
82
2
84
82
81
82
4
80
78
80
79
3
78
77
80
78
4
Linear Fluid System (Linear Flow System)
206
160
133
166
44
214
166
156
179
32
212
171
159
181
29
200
178
135
171
38
208
159
138
168
42
214
165
148
176
38
226
178
171
192
29
220
194
174
196
twenty three
223
193
182
199
twenty one
3.4 Mainstream smoke (K3R4F research cigarettes)
The comparative experiment of cigarette smoke further confirmed the results obtained in the previous experiments. The data is shown in Table 5. As shown in the data in Table 5, we can analyze that the particle deposition in the linear flow exposure system has very large instability, high data deviation, and the radiation flow exposure system has a very stable and repeatable particle deposition effect.
4. Discussion
When the test substance is a gas, it is not important whether the cell culture chamber and the aerosol inlet are linearly arranged because the distribution of the gas is uniform. However, when the test object is a particulate aerosol, its linear direction transport will have a very large influence on the deposition of particulate matter due to its complex particle size distribution and physicochemical properties. (1) The concentration of particles and the distribution of particle size have an effect on the stability of the dilution system; (2) the concentration and particle size of the particles deposited on different cell compartments will change, resulting in the deposition of particles in different cell compartments. Parallelism and repeatability are poor. Obviously, the dilution of the intake air of the compressed air is unable to break the laminar flow distribution of the test substance, which will not change the deposition effect as described above.
In view of these shortcomings, the cell culture chamber and aerosol inlet distribution need to be fundamentally changed. In order to avoid the unevenness of the exposed particles, Cultex introduced a new concept of the second generation of exposure to the Cultex RFS module. Here, the aerosol will enter through a central inlet with a nozzle (Mohr, 2013) where the aerosol will be evenly dispersed into the channels of the three central radiation distributions, through which the cells enter the radiation-distributing cell culture chamber. After such a process, the uniformity and repetition of aerosol deposition in the three cell compartments will be greatly enhanced. The pictures and data results after deposition of different particles in this experiment showed very good results, and the particle deposition deviation and standard deviation between the three cell compartments were very satisfactory. Compared with the first-generation linear flow system, we found that the second-generation radiation flow exposed the poisoning module lost some of the particles, that is, the total mass of deposited particles in each cell was reduced. This is due to the fact that we have added large particle (agglomerated particle) pre-separation technology in the Cultex RFS module, which reduces the possibility of depositing large or condensed particles on the cell surface, ie improving the uniformity of the particle size distribution and making the experiment The test substance is more stable. It not only reduces the influence of coarse particles on the experiment, but also further improves the experimental repeatability and stability.
In conclusion, the design optimization of the structure of the in vitro exposure system plays a decisive role in the improvement of the reproducibility of the in vitro exposure test, and has epoch-making significance in the in vitro exposure technology.
Pvc Cling Film,Cling Film Food,Cling Film Roll,Pvc Food Wrap Film
DONGGUAN YEE HUP TRADING CO,.LTD , https://www.yeehupacks.com